AI has become really hot these days. Everybody seems to be talking about singularity, Alpha Go, potential AI take-over. What is AI exactly and how will AI be used in our lives? This article will try to talk about the very basics.
如今人工智能似乎成了大众最热情又最陌生的话题,当外行人谈人工智能、谈AlphaGo大战柯洁、谈机器人、谈各种科幻电影时内行人在谈什么?或者说如何装作内行的样子?这篇文章将告诉你谈论人工智能的正确打开方式。
Glossory
概念
Artificial Intelligence
AI is the broadest term, applying to any technique that enables computers to mimic human intelligence, using logic, if-then rules, decision trees, and machine learning (including deep learning).
人工智能是最广义的概念,用于描述任何模拟人类智能技术,包括逻辑、if-then规则、决策树、机器学习(包括深度学习)等方法,其中机器学习和深度学习是人工智能中重要的部分。
Machine Learning
The subset of AI that includes abstruse statistical techniques that enable machines to improve at tasks with experience. The category includes deep learning.
机器学习
是人工智能的子集中利用统计方法让机器随着经验的积累在特定任务上的表现能不断提高的技术,该领域包括深度学习。
Deep Learning
The subset of machine learning composed of algorithms that permit software to train itself to perform tasks, like speech and image recognition, by exposing multilayered neural networks to vast amounts of data.
深度学习 作为机器学习的子集,是一种利用多层神经网络处理大量数据的算法,通常用来处理语音和图像识别的问题。
Machine Learning
机器学习
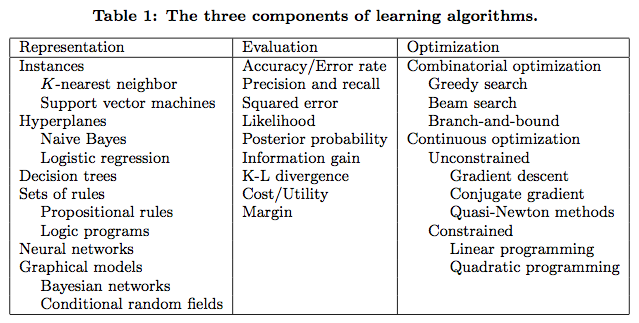
First, let’s talk about machine learning. Each machine learning algorithm has three components: representation, evaluation and optimization.
首先我们说说机器学习,它由三部分组成:表示(模型)、评价(策略)和优化(算法)。机器学习方法的不同,往往是这三者中的某些项不同。
Machine learning can be seperated as supervised learning, unsupervised learning and reinforcement learning. Each has its different applications.
按使用方式分类的话,机器学习通常分为监督式学习、无监督学习和增强学习三种,每一种方式的应用都不一样。
Supervised learning is the machine learning task of inferring a function from labeled training data, includes classification and regression. In chatbot design, intent recognition and entity extraction are in this category.
监督式学习主要是通过标注数据归纳输入和输出的关系,预测新的样本,包括分类和回归。比如:”用户说话的意图是什么?打车还是咖啡”,“用户这个月下单金额可能会是多少?”。
Reinforcement learning refers to agents taking actions in an environment so as to maximize some notion of cumulative reward. In chatbot design, dialogue state management can be applied.
增强学习主要采取不同的动作最大化奖励函数。用于对话状态控制,生成不同回复或者调用不同的API。
Unsupervised learning is the machine learning task of inferring a function to describe hidden structure from “unlabeled” data, includes clustering, anomaly detection, dimensionality reduction and Generative Adversarial Networks. In chatbot design, generating user intents, detecting fraud users and profiling VIP user can be seen as unsupervised learning.
无监督学习主要从非结构化的数据中寻找隐藏结构,没有明确标准,包括聚类、生成、异常值检测、降维等方法。能解决“使用日程的用户有多少种类型”、“生成一系列以假乱真图片 ”、“这个用户是不是诈骗用户”、“如何快速对VIP画像”等问题。
Deep Learning
深度学习
Deep learning allows computational models that are composed of multiple processing layers to learn representations of data with multiple levels of abstraction. It can be used to represent any function in the world without the burden of feature engineering. Its performance can go up along with the amount of data available.
再说回到上文提过的机器学习的子集——深度学习,深度学习是一种通过多层网络来进行结构性的特征变换,能利用海量数据减少大量特征工程的一种模型。深度学习可以模拟任何函数,其表现能随着数据量的不断提高而提高,在海量数据的情况下效果优于传统机器学习方法。
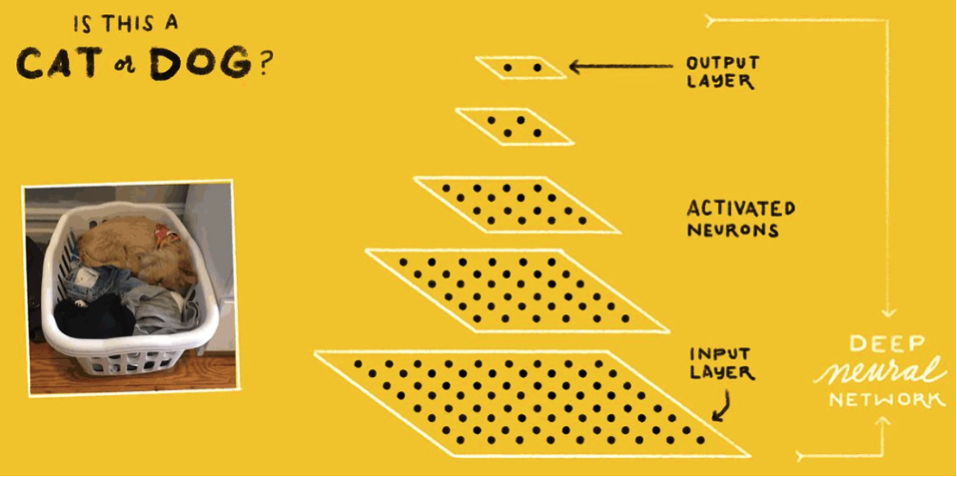
There are different types of Neural Networks, including DNN(Deep Neural Network),CNN(Convolutional Neural Network)andRNN(Recurrent Neural Network), each with its different variations. For example, CNN is usually used in CV and RNN is usually used in NLP.
它有很多种网络架构,常见的包括DNN(Deep Neural Network)、CNN(Convolutional Neural Network)andRNN(Recurrent Neural Network),这些网络架构也有很多变种,分别可以用来处理不同的问题。比如CNN往往用来处理图像识别,RNN往往用来处理有时序依赖的任务。
The history of deep learning can be traced back to 1943, but its recent emergence has a lot to do with the three computer scientists, Yann LeCun from NYU, Geoffrey Hinton from the University of Toronto and Yoshua Bengio from Université de Montréal. They invented new models and designed new tricks to make deep learning really start to work. Also, they trained a lot of students into this field.
深度学习早在1943年就被提出,它的兴起和深度学习三巨头的推动密切相关,他们是Yann LeCun 杨立昆 (NYU大学教授,Facebook AI研究院(FAIR)主管)、Geoffrey Hinton 杰夫·欣顿(多伦多大学教授,Google工程院士)和Yoshua Bengio约书亚·本希奥(蒙特利尔大学教授)。他们发明或者改进的方法让深度学习真正可使用,同时为这个领域培养了大量人才。
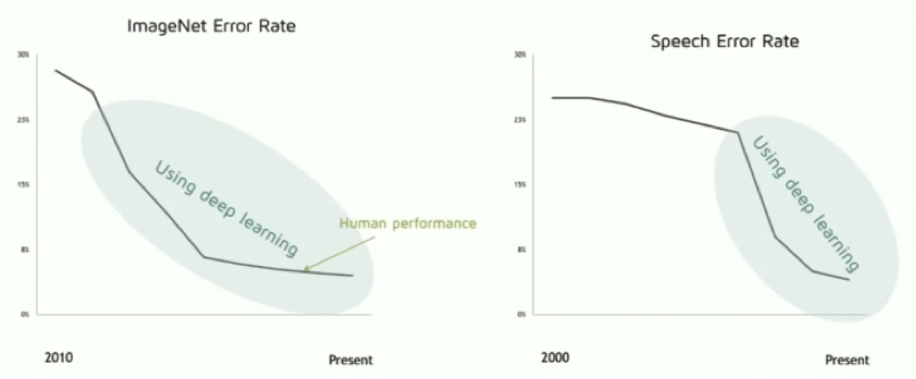
Deep learning started to get mainstream attention in 2012, when Krizhevsky, the student of Geoffrey Hinton, reduced the error rate of ImageNet from 26.2% to 15.4%, using deep learning method. Based on the paper, other researchers improved the method and pushed the performance to super human level in 2015. Deep learning achieved similar amazing performance in speech recognition and many other areas.
深度学习真正进入主流研究者的视野是在2012年,Geoffrey Hinton的学生Krizhevsky利用深度学习将ImageNet挑战的错误率从26.2%下降到了15.4%。其它研究者在该研究的基础上,利用更新的深度学习方法如残差网络等来提高表现,15年的冠军在测试集上的表现已经超越人类水平。 同时在语音识别中,深度学习也有类似出众的表现。
Current Progress of AI
人工智能的现状
Academia has pushed the development of AI to a new level. Unlike the omnipotent AI in some Sci-Fi films, the general purpose strong AI still has a long way to go. In contrast, weak AI, which is good at solving problem in a narrow domain, has made great progress thanks to the improvement of data, algorithm and computing power. AlphaGo is a good example.
学术上的进步推动了人工智能的发展,但和电影里似乎无所不能的人工智能不一样,当前强人工智能,即所谓通用跨领域的、超越人类的智能依然遥遥无期。而能解决局部问题的弱人工智能,依靠基于统计方法的机器学习取得了重要进展。而这种进步主要来自于数据、算法和计算能力的大幅增长,其代表就是2016起分别击败李世石和柯洁的Alpha Go。
The creation of artificial intelligence is still very dependent on human wisdom. Even in deep learning, the performance of the algorithm is also greatly dependent on the wisdom of the designer. There is a joke “how much human effort, how much artifical intelligence.” At present, some researchers are experimenting on how meta algorithm can design other algorithm, but it is still in the laboratory stage.
当前人工智能的创造仍然极大依赖于人的智慧,即使在深度学习中,算法的表现也极大依赖于实现者的智慧,行业里戏称“有多少人工,就有多少智能”。目前有些研究者在实现如果实现让算法来实现算法,但仍在实验室阶段。
Application of AI
人工智能的应用
What can we do with artificial intelligence? The current breakthrough is mainly from supervised learning (and some data rich reinforcement learning): from X to Y, highly repetitive, contains a lot of data and computational work. The learner trains a model through a lot of tagged samples, and then predicts the new unseen data based on the model. This method is heavily dependent on high quality labeled data.
我们能利用人工智能技术做什么?目前突破主要还是来自监督式学习(和容易获得数据的增强学习):从X到Y,重复性强,包含大量数据和计算的工作。 算法通过线下训练样本训练了一个模型,之后对新的未知数据进行预测,这种做法大量依赖人来进行高质量的标注。
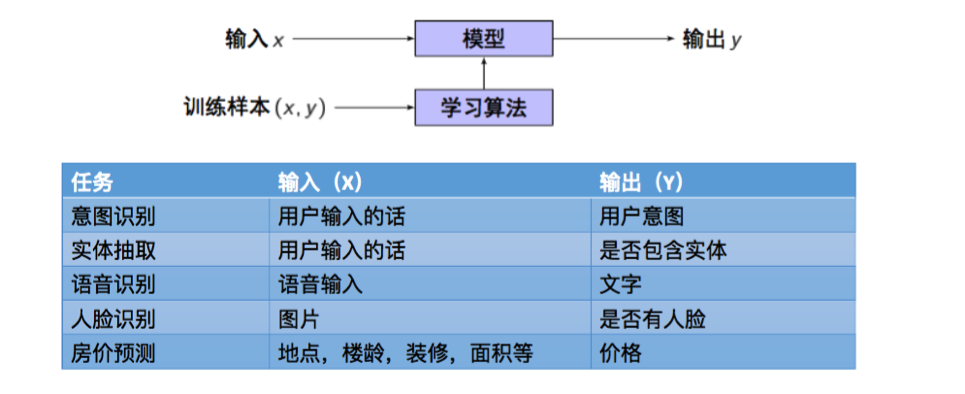
Artificial intelligence in narrow sense includes three parts: automatic speech recognition, computer vision and natural language processing. Currently, artificial intelligence is good at perception tasks, which is to find representations of vocal and visual signals. At present, many teams are using artificial intelligence to deal with cognitive tasks, trying to find appropriate representations of words, sentences or more abstract concepts.
狭义的人工智能包括语音、视觉和自然语言处理三部分。当前人工智能处理的比较好的是感知类任务,即识别并转换语音、视觉等信号。目前很多团队在试图用人工智能来处理认知任务,将文字或图像抽象为对应表示。

A broader sense of artificial intelligence includes recommendation systems, computational ads, robotics and many other fields. When large amounts of data are available, artificial intelligence is suitable for helping people make decisions, in the case of personal assistants, news recommendation, automatic driving and so on.
更加广义的人工智能还包括推荐系统、辅助决策和机器人。在拥有大量数据的情况下,人工智能也适合处理决策任务,辅助人或者自动选择最优的行动,并根据信号反馈优化自己的算法,常见方向包括新闻推荐、自动驾驶等等。
