For five components in dialogue system: Automatic speech recognition(ASR), Natural language understanding(NLU), Dialogue management(DM), Natural language generation(NLG) and Text-to-speech synthesis(TTS). ASR are relatively well solved by deep learning technology. NLG and TTS are easy to control. The difficulty of dialogue system design lies mainly in NLU and DM, which will be discussed in details in following paragraphs.
Natural language understanding (NLU)
The goal of NLU is to convert text into semantic representations. Exact meanings of the words in the text are not important. What matters is the semantic information the text conveys. NLU is also known as semantic decoding.
NLU is challenging for several reasons such as speech recognition error, ambiguities, disfluencies:
- For speech recognition, though great progress has been made, there are still word error rate around 10-20% depending on the context.
- Natural language is also notoriously difficult for its ambiguities. There are cases like user said the following at 1am: 明早8点叫我起床. It is difficult for dialogue system to know it is this afternoon 7 hours later or it is the literally the morning tomorrow.
- Also, in many cases, user will choose confusing expressions. They sometimes correct themselves by saying “25号中午提醒我打电话给 ,哦不,26号” or they repeat themselves by saying “我要一个, 一杯中杯拿铁送到公司”. Both cases can be challenging for computers.
Semantic representation
Dialogue act: combination of dialogue act type followed by a sequence of dialogue act items:
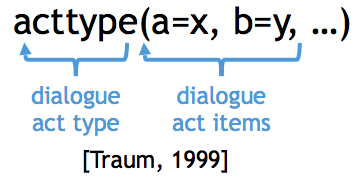
Example:

NLU approaches
There are two different approaches to attack this problem: by rule or by statistics.
-
Rule-based approach Rules define how to extract semantics from text. The benefit for rule-based approach is semantic representation can be flexible and it does not require training data. But it will require large number of rules to cover different scenarios and it is hard to maintain as the number of rules grows
-
Statistical approach In this approach, people train statistical models on annotated data. There are two typical tasks: intent classification, which determines intention of the user, and sequence tagging, which identifies probability of a word/character being part of a concept. For statistical approach, training data is required and it might be difficult to explain and hard to tune. However, when there are more data, performance will also be better and system will be more robust.
In practice, rule-based and statistical approaches are combined.
NLU as a service
NLU as a service defines common modules in any NLU systems. For example , intent identification and entity extraction. Service provider prepared annotated data and built the modules using data-driven approaches.
Existing NLU services includes WIT.AI (Facebook), API.AI (Google) and LUIS.AI (Microsoft).
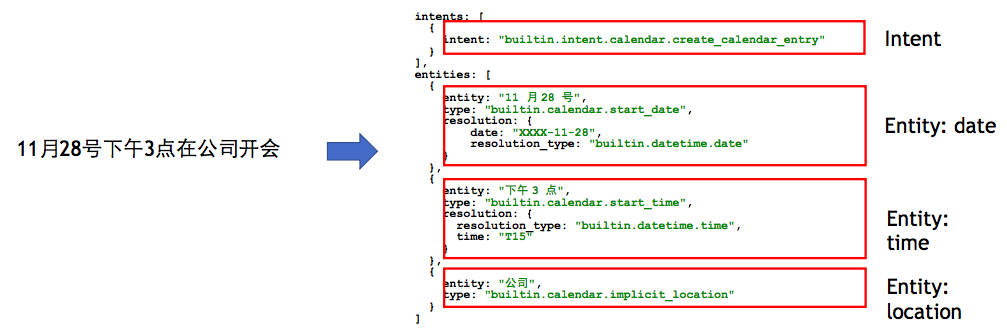
NLU example from LUIS.AI:
Dialogue management (DM)
DM is the “brain” in dialogue system. A dialogue manager will update dialogue state and select one or more selected system action(s):
-
Task1: dialogue state update
• Dialogue state encodes every information relevant to the system
• DM maintains a representation of the current dialogue state
• DM updates the dialogue state as new information becomes available -
Task2: action selection
• Make decisions on which actions to take based on dialogue state
DM approaches
We will introduce 4 different approaches to dialogue management: finite-state machine, frame-based approach,statistical approach and end-to-end neural network learning approach.
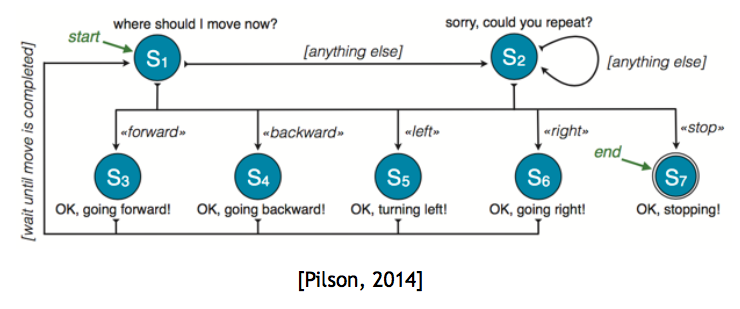
Finite-state machine
For some simple closed domains tasks, dialogue space can be limited. It is possible to use a finite-state machine to model the conversation experience.
- Each state is associated with a specific action to execute at that state
- Each edge is labelled with a condition on user input
- Maps <state, user input> pairs to the next state
It is easy to build with high accuracy rate, but it is difficult to scale to complex domains.
Frame-based approach
For task fulfilling dialogues, user needs to submit a form with relevant information. In this case, frame-based approach is appropriate.
- Frame is a set of slot-value pairs
- Frame is gradually filled by the user inputs
- A set of rules determine which action to take after each user move
This approach is also easy to build It is difficult to extend to other domains and unable to handle uncertainties of dialogue state.

Statistical approach
In statistical approach, POMDP(Partially Observable Markov Decision Process) is usually used as the math model.
- Agent knowledge is represented by belief state: probabilities over all possible states
- The optimal action maximizes the expected reward for the agent
- A policy maps belief state to the optimal action
- The optimal policy can be obtained by reinforcement learning
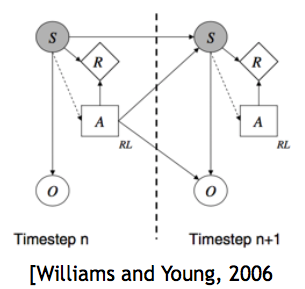
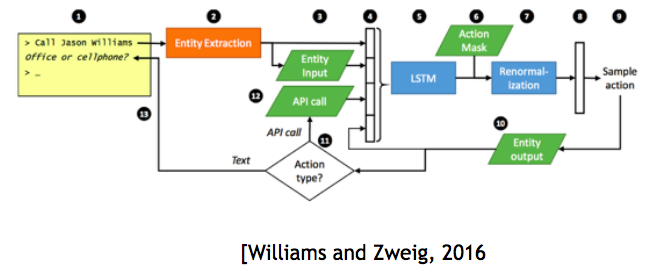
End-to-end neural network learning approach
In the neural network approach, deep learning is introduced to allow for end-to-end learning and it saves engineering time.
- The neural net automatically infers a representation of dialogue history
- NLU outputs and previous actions are inputs for the neural net
- Outputs of the neural net is a probability distribution over all possible actions
- Weights for the neural net can be learned by supervised learning or reinforcement learning